Continuous value prediction
Introduction
This tutorial provides a step-by-step guide to using Renesas's Reality AI Tools portal for building AI models in non-visual sensing applications. We will work with a continuous value dataset collected from a vibration sensor to predict exact numerical values rather than categorical classifications.
Objectives
By the end of this tutorial, you will:
- Gain hands-on experience with the Reality AI Tools – Values module.
- Learn how to analyze and develop machine learning models for non-visual sensing applications.
Requirements
Hardware & Software
- A PC or MacBook with Chrome or Firefox installed.
Dataset
- 250 CSV files containing continuous value data. Click here to download: CV Prediction Dataset
- 1 metadata.csv file. Click here to download: CV Prediction Metadata
Estimated Time
60 minutes
Step 1: Creating a Project and Uploading the Dataset
Step 1.1: Accessing Reality AI Tools
- Open your web browser and go to: portal.reality.ai.
- Enter your login credentials (provided via email) and click Login.
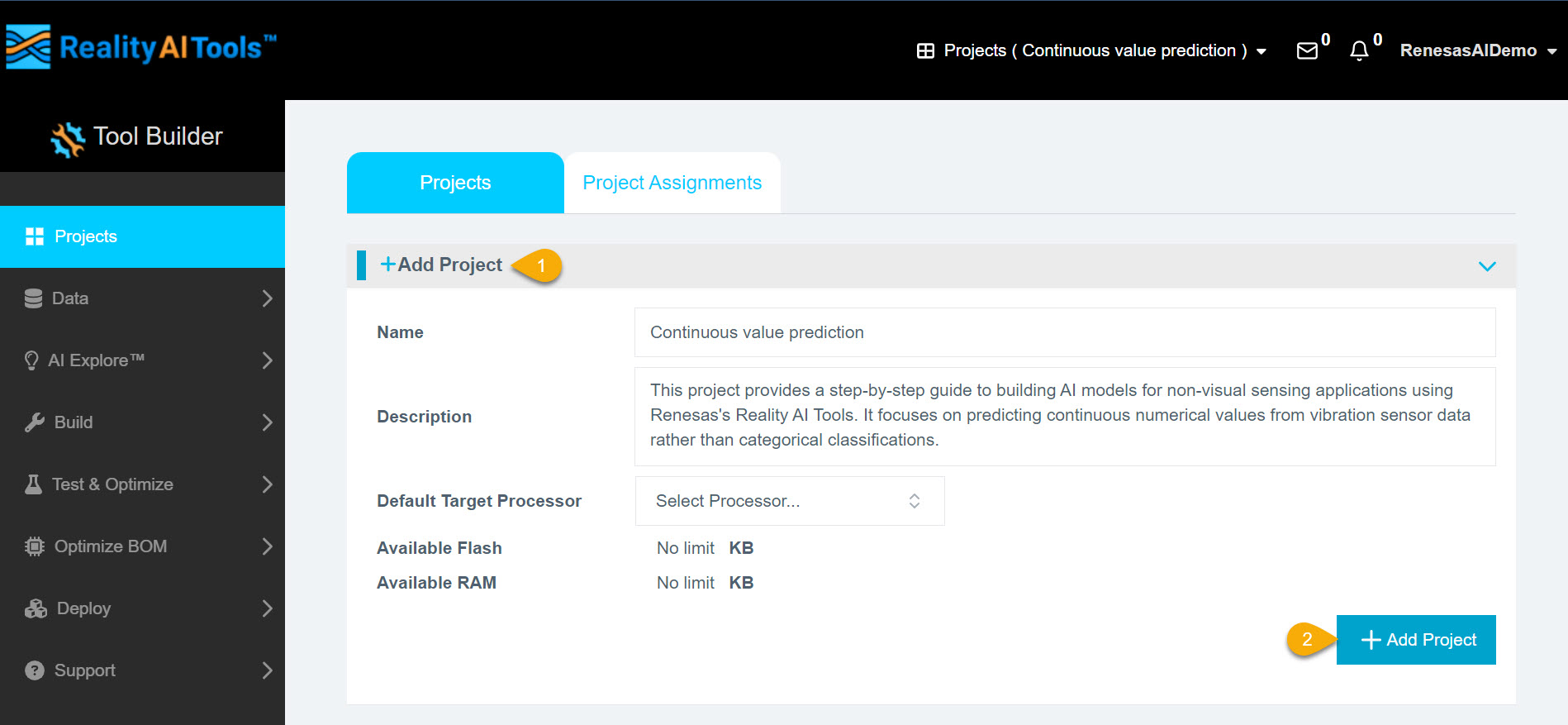
Step 1.2: Creating a New Project
- After logging in, the Reality AI Tools portal will open with no projects listed.
- Click Add Project and enter the following details:
- Project Name (required)
- Description (optional)
- Click Add Project to proceed.
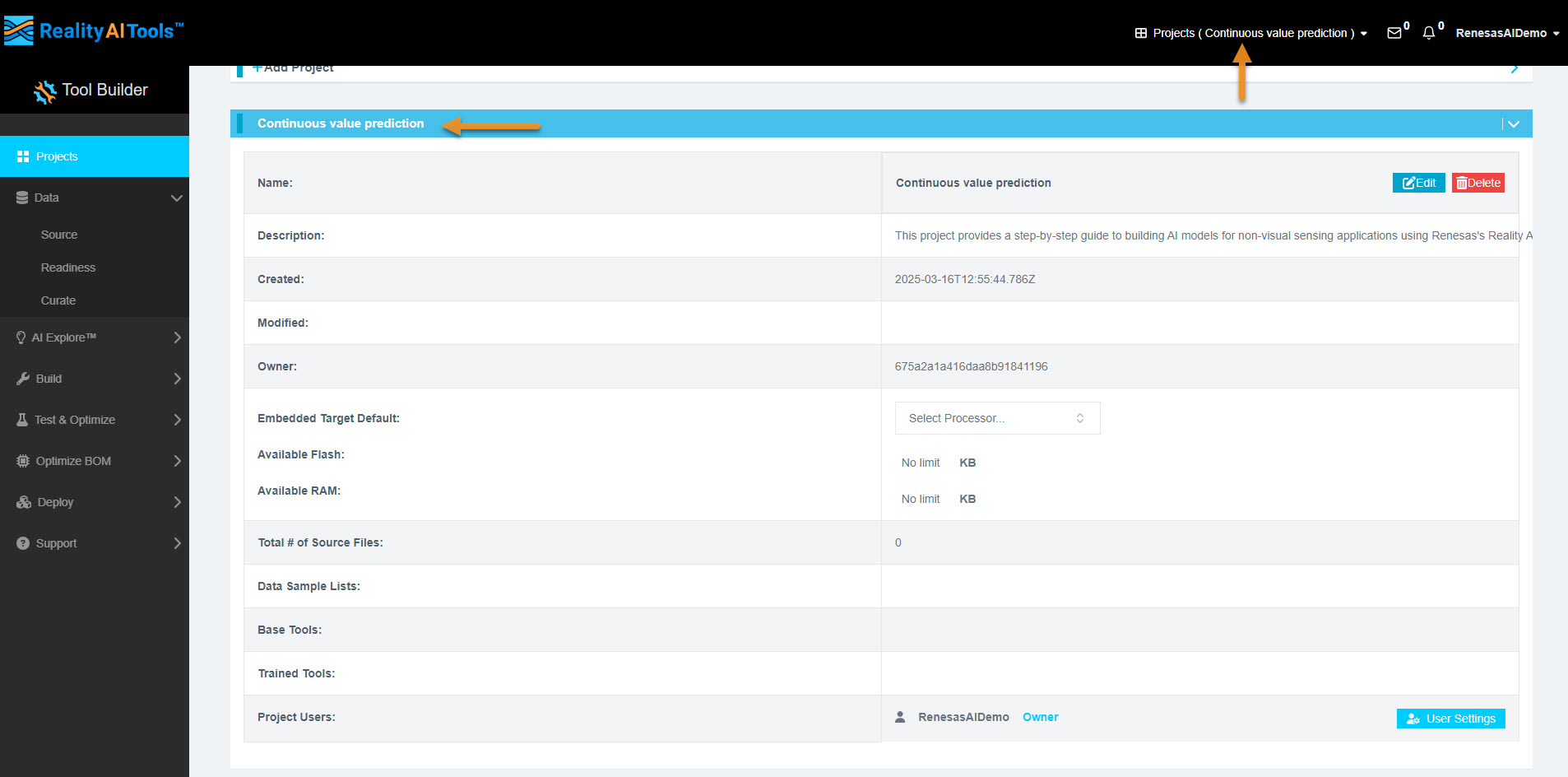
Step 1.3: Selecting the Project
- Once the project is created, click its name to open it.
- This will allow you to manage datasets and perform various analyses.
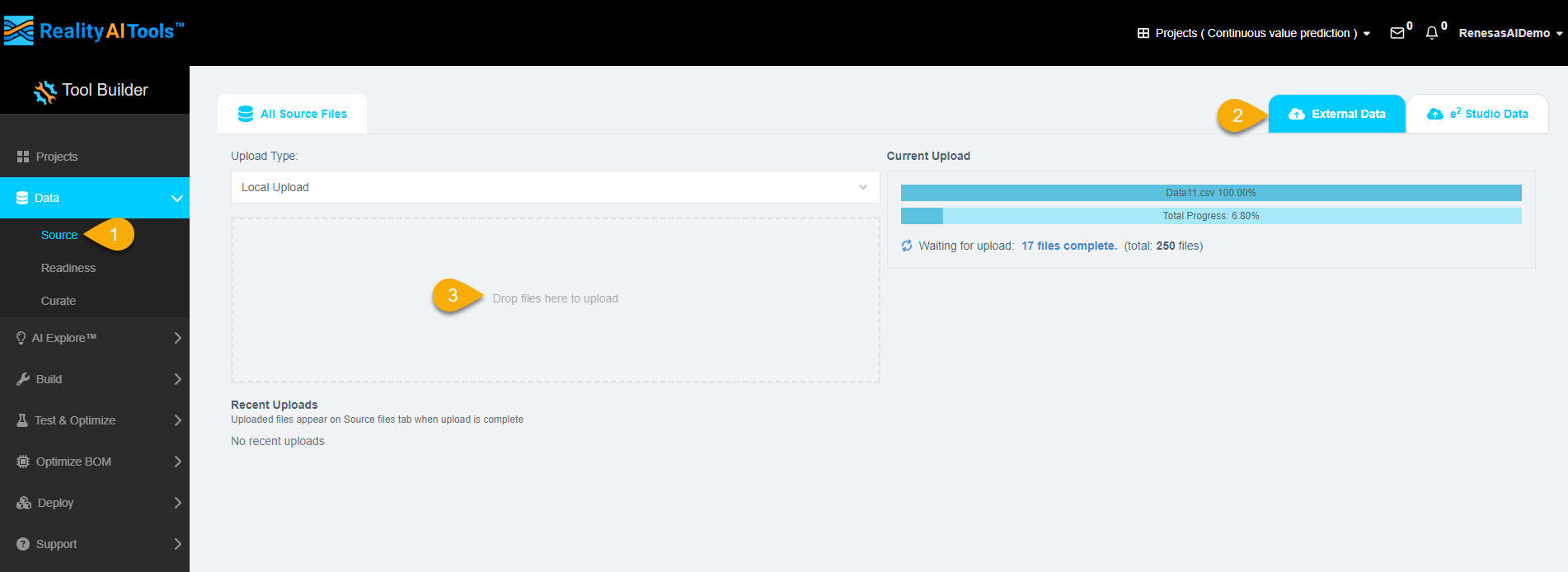
Step 1.4: Uploading the Dataset
- In the left menu, click Data > Source.
- Navigate to the External Data tab.
- Click Drop file here to upload and select the dataset files.
Step 1.5: Selecting Files for Upload
- Navigate to the downloaded dataset folder.
- Select all 250 data files.
- Click Open to upload them to the portal.
- The file upload progress will be displayed on the page. Wait for all files to be fully uploaded.
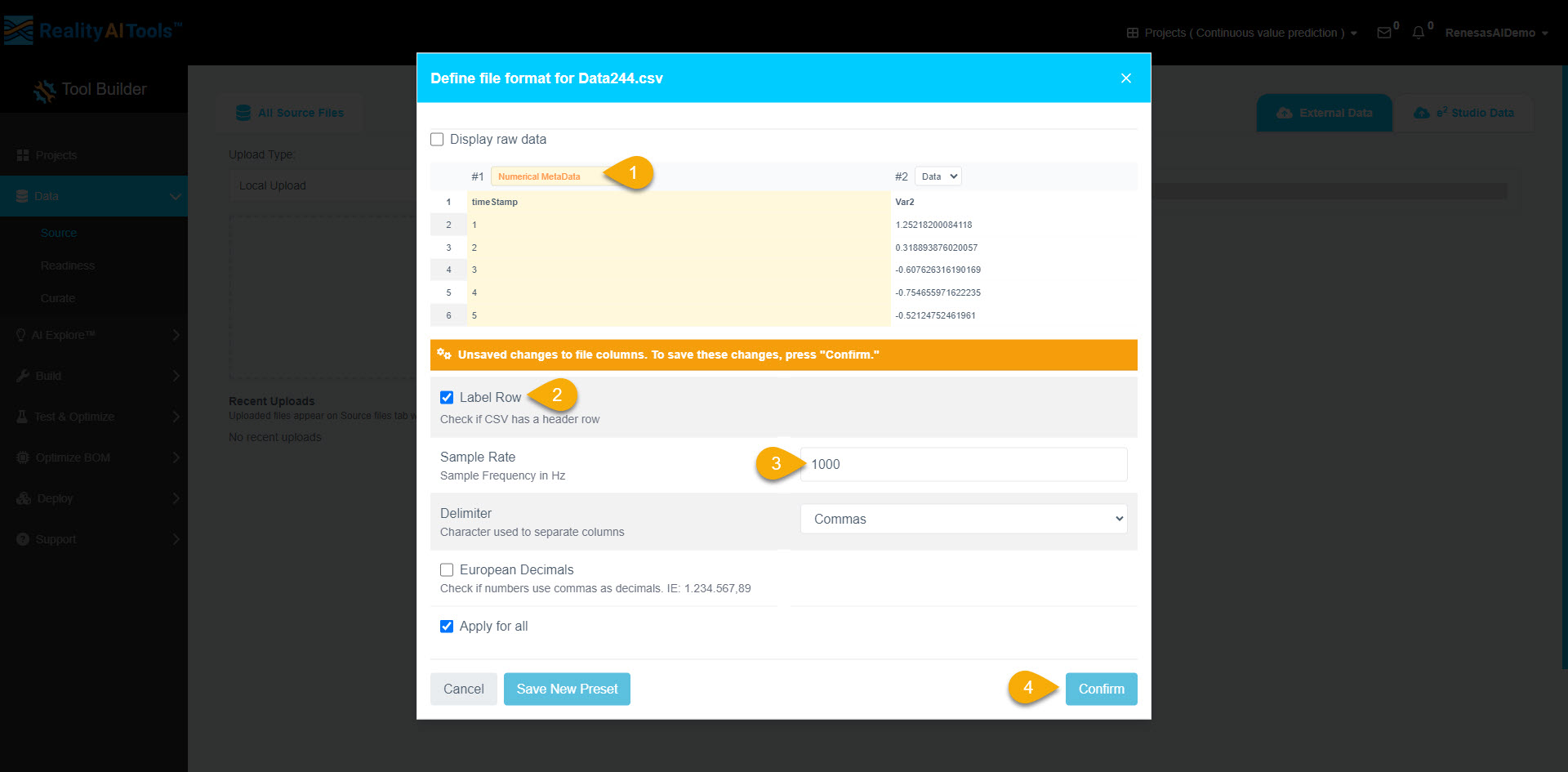
Step 1.6: Formatting the Dataset
- Once uploaded, a formatting window will appear.
- Click Data > Numeric Metadata to label the first column of the dataset.
- Select the Label Row checkbox.
- Set the sample rate as 1000 Hz.
- Click Confirm to apply formatting to all files.
- The dataset is now uploaded and formatted successfully.
Step 2: Curating and Preprocessing Dataset
To prepare the dataset, break the data files into smaller segments. These segments serve as inputs for the machine learning (ML) model.
For example:
- If a data file is 10 seconds long, split it into ten 1-second segments.
- Adjust the segment length based on prior knowledge or experimentation.
- For this tutorial, use a 1-second window length.
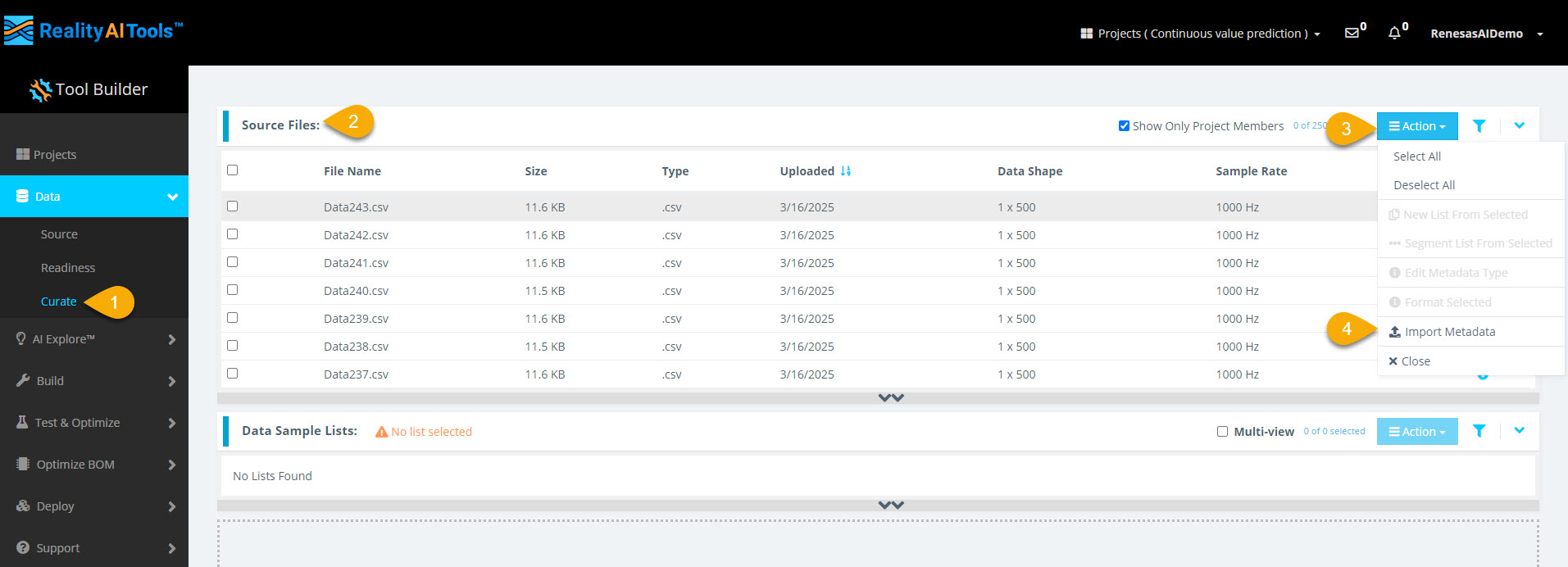
Step 2.1: Navigate to Curate Options and Import Metadata
- In the left menu, select Data > Curate.
- Select the Source Files tab to expand the section.
- Select Action > Import Metadata to assign labels (Ground Truths) to the data files.
- Select the file upload space to open the file explorer.
- Select metadata.csv from the dataset directory.
Step 2.2: Assign Target Value Labels
- Set the first dropdown to File Names.
- Set the second dropdown to Target Value to label the files correctly.
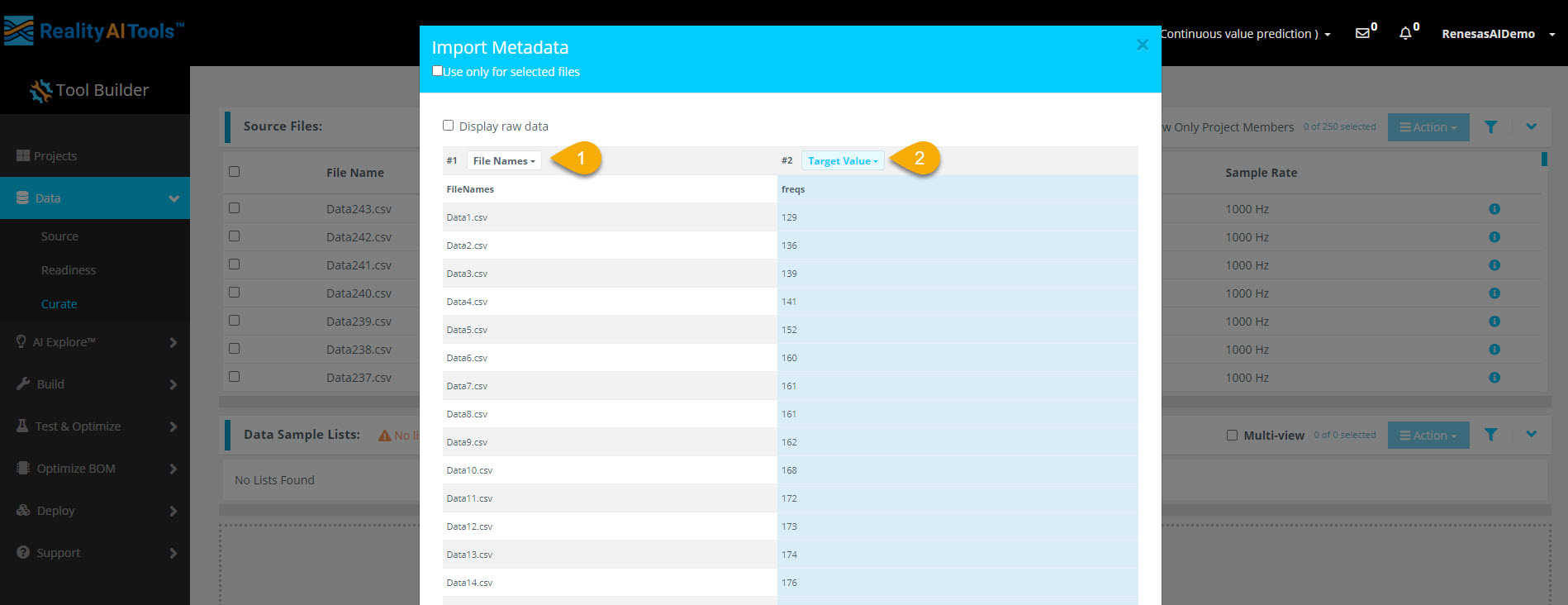
Why Use Target Value?
- Target Value represents labels for continuous value (regression) problems in ML.
- The model recognizes only Target Class or Target Value for labeling and Data for sensor readings.
- Other metadata like time, date, and numeric values help with sorting but do not affect model training.
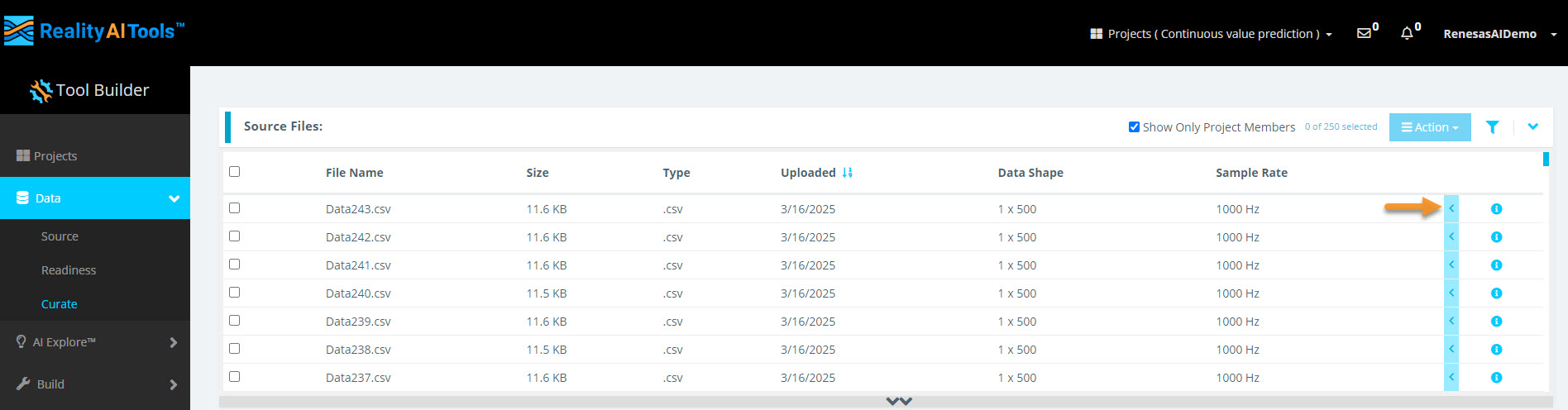
Step 2.3: Verify Assigned Labels
- Select the blue arrow next to a file name to view the assigned labels.
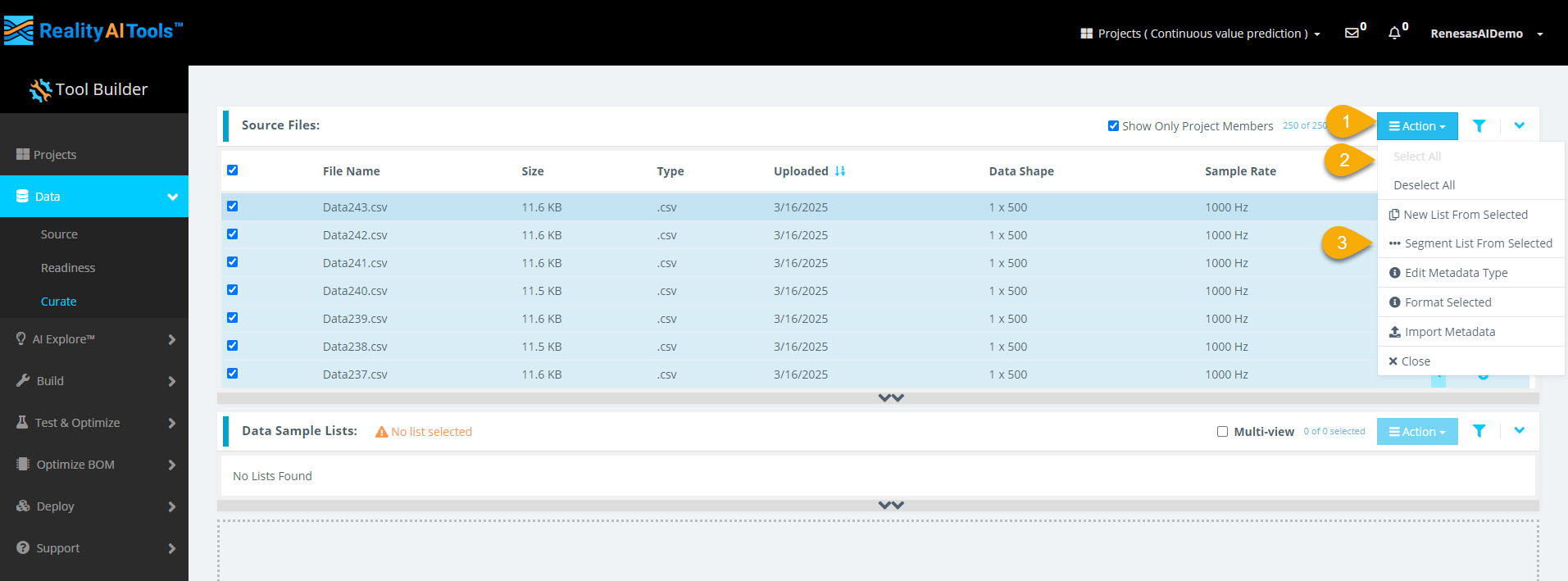
Step 2.4: Select Files for Segmentation
- Select Action > Select All to choose all files.
- Select Action > Segment List from Selected to open the segmentation window.
Why Segment the Data?
- ML models on Renesas MCUs operate in resource-constrained environments.
- They must process live data efficiently in small time windows (e.g., 1 sec, 500 ms).
- Instead of analyzing long data streams, breaking data into smaller segments helps the model adapt to real-world conditions.
Step 2.5: Configure Segmentation Parameters
In the segmentation window, enter the following details:
- Target Reduction Method:
Mean - Window Length:
1000 milliseconds(1 sec) - Offset:
1000 milliseconds(1 sec)
After entering the parameters:
- Enter a name in the Output Sample List field.
- Select Submit to start segmentation.
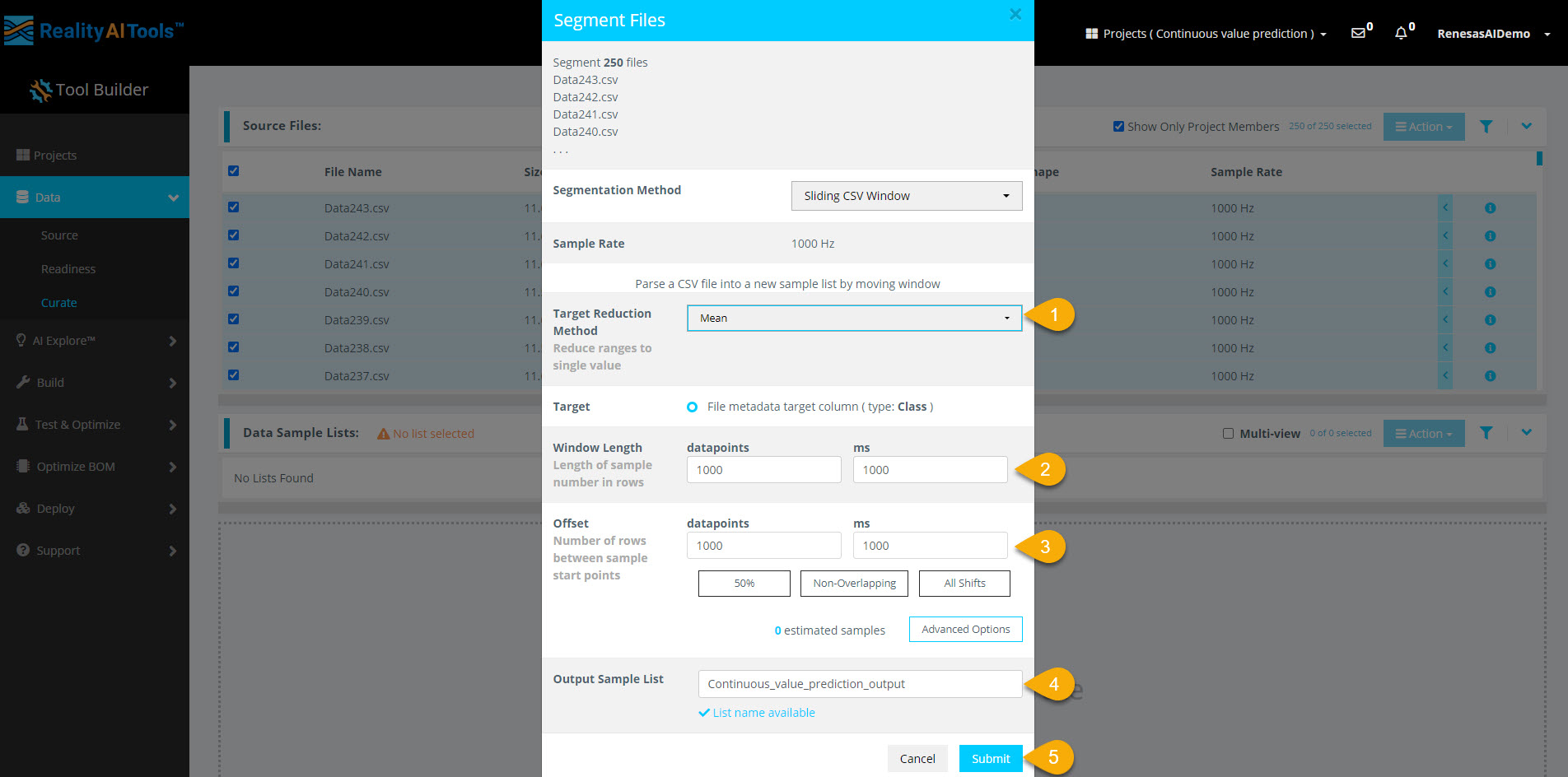
Here,
- Window Length: Defines how much data the model analyzes for classification.
- Offset: Sets the gap before creating the next segment.
- A 50% overlap balances data variation and redundancy.
- Non-overlapping windows work best with large datasets.
- Offset = 1 (All Shifts) is useful for testing after selecting a classifier.
Step 2.6: View Processed Data
- Wait ~30 seconds, then refresh the page.
- Select the Data Sample List tab to view the processed segments.
- Select a sample to Curate and analyze its histogram.
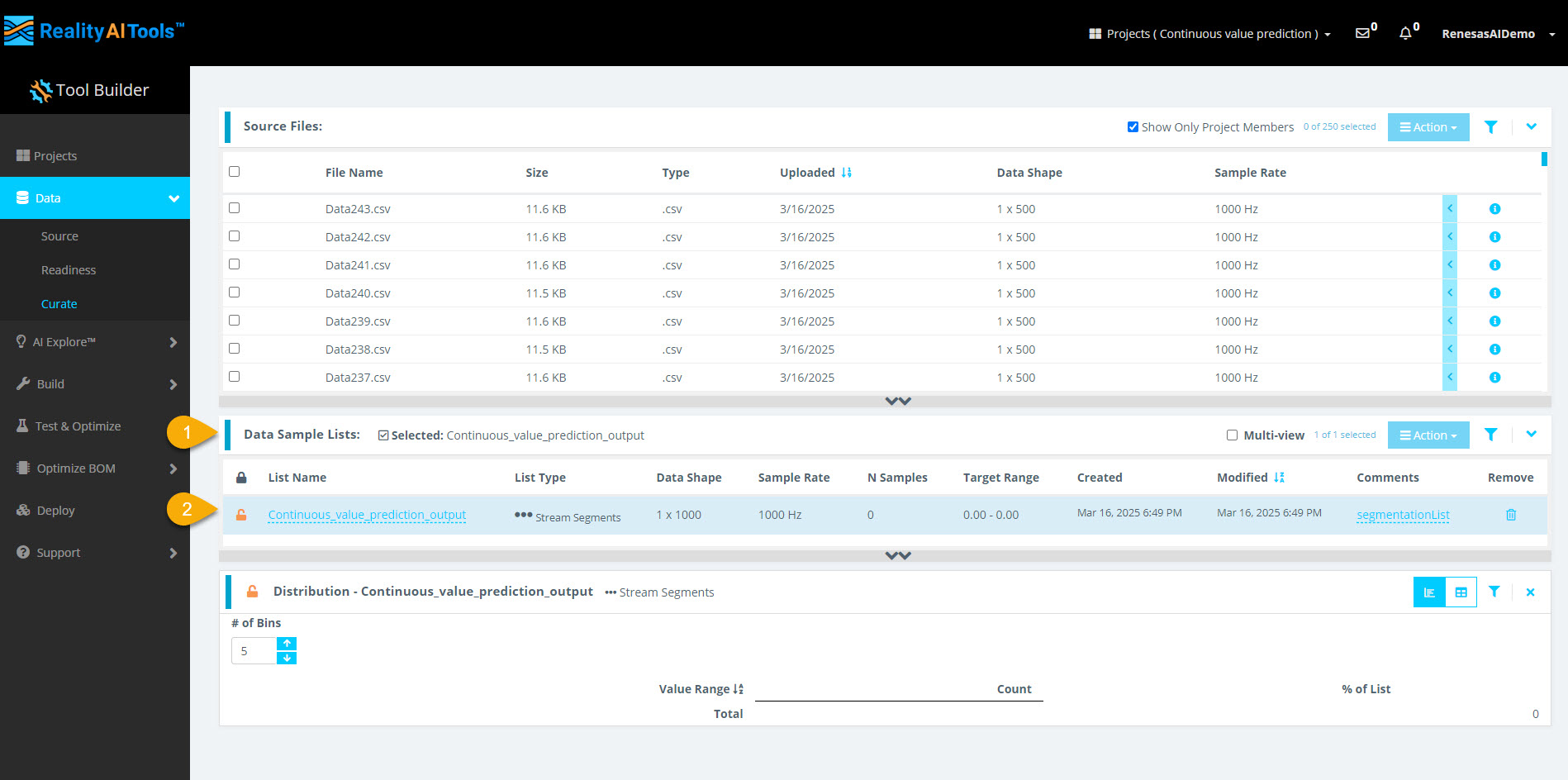
- The segmentation process takes less than 1 minute for small datasets.
- Larger files (e.g., 1 GB) may take 5-10 minutes to segment.
- If the histogram does not appear immediately, refresh the page.
- The dataset is now curated and preprocessed successfully.
Step 3: Analyzing Data and Creating Initial Models
In this section, you will create AI models using the uploaded dataset and analyze various statistics for those models.
Step 3.1: Create Initial Models
- In the left menu, click AI Explore.
- Click Values and RUL.
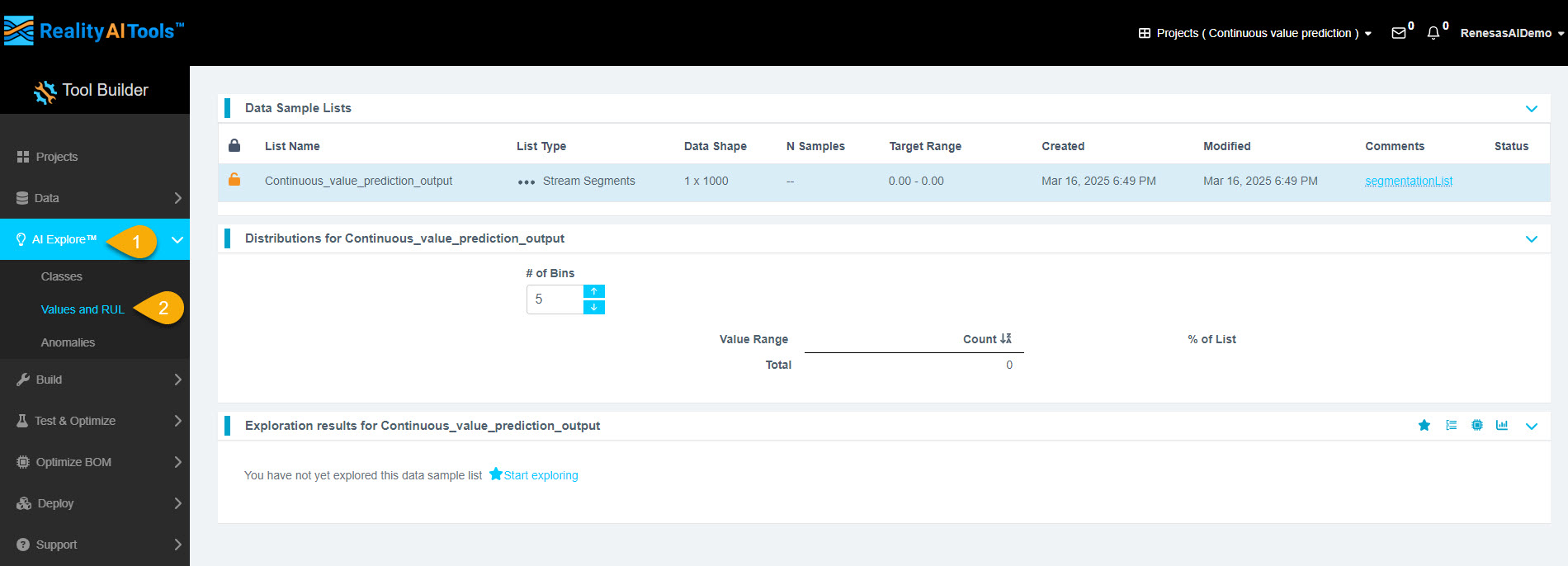
Step 3.2: Choose the AI Model Type
Reality AI Tools provides three types of AI models:
- Classes: Use when you have labeled categorical data. This is for classification models that use supervised learning.
- Values: Use when your dataset contains discrete integer or float values instead of categories. Examples include machine temperature or tire pressure. This is also supervised learning. (This tutorial uses this option.)
- Anomalies: Use for anomaly detection. This is a semi-supervised model that requires only normal data to create a baseline model.
Click the segmented list once you are on the Classes page.
Step 3.3: Start Model Exploration
- Click the list.
- Click Start Exploring to generate models.
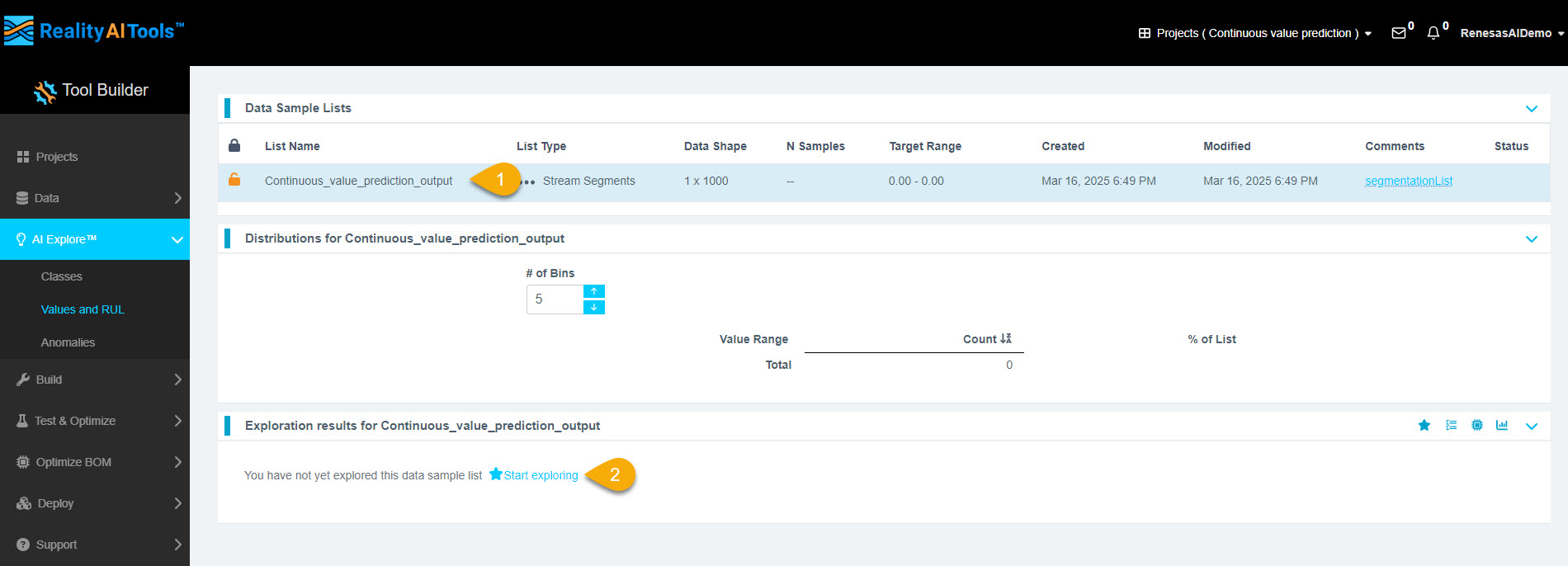
Step 3.4: Monitor Model Generation Progress
You will see the progress of the model generation process.
What Happens in the Background?
- Clicking Start Exploring triggers the Reality AI algorithm to analyze your data.
- The algorithm creates optimized feature sets and machine learning models that best fit the classification problem.
- It displays the best-performing models.
How the Algorithm Works
- AI Explore finds the best feature sets and machine learning parameters.
- Promising feature sets are used to construct machine learning models.
- Models are trained on a sub-sample and validated using K-Fold validation.
- Only the top-performing models are displayed.
What is K-Fold Validation?
K-Fold validation splits a dataset into K sections. Each section is used as a testing set once, while the remaining sections train the model.
For example, in 10-Fold validation (K=10):
- The dataset is split into 10 folds.
- In each iteration, one fold is the test set, and the remaining folds train the model.
- This process repeats until all folds have been used as test sets.
AI Explore uses K=10 for model evaluation.
Step 3.5: View Model Performance
As the system explores feature spaces, the top-performing models appear on the page.
Step 3.6: Analyze Model Results
- In the Exploration Results section, each row represents a different model based on features identified during AI Explore.
- Click Confusion Matrix to view detailed accuracy statistics.
Step 3.7: View Confusion Matrix and Regression Plot
- The Confusion Matrix/Regression Plot pop-up appears.
- Click the second option at the bottom for detailed statistics.
Note:
- The first option shows a confusion matrix with overall accuracy and error distribution.
Step 3.8: Analyze Error Distribution
The error distribution plot helps visualize error concentration across the numeric range.
- A wider distribution indicates poor model performance.
- The Regression Plot (Actual vs. Predicted) for the first model appears at the top.
- The sample-wise residual errors plot appears below.
What is Residual Error?
A residual is the vertical distance between an observed data point and the regression line. It represents the prediction error.
What is R²?
R-squared (R²) measures how well a regression model explains the variation in the dependent variable.
What is MAE?
Mean Absolute Error (MAE) is the average of absolute errors in predictions.
Step 3.9: View Resource Consumption
Hover over the complexity tab to view estimated resource consumption.
Understanding Complexity Numbers:
- X operations: Multiplication operations required for the model.
- Feature Space: Operations needed for feature calculations.
- Classifier: Operations required for predictions. (This is blank for regression models.)
- Total: Sum of all operations.
Step 3.10: Interpret Complexity Numbers
- Complexity numbers estimate resource consumption on the MCU/MPU.
- They are not final and can be optimized.
- Example: If a model focuses on frequency bands less than 50 Hz, filtering out unnecessary data can reduce resource use.
- If a target processor was preselected, top models will fit within its resource limits.
Step 3.11: Deploy the Model
After reviewing the statistics:
Click Deploy Model for further testing and export.
Step 3.12: Name and Save the Model
- Enter a name for the exported model.
- Click Add.
Step 3.13: Verify Deployment
- The deployed model's icon changes to indicate success.
- Hover over the icon to view the model name.
- If the deployment fails, contact customer support.
You have successfully completed this section.
Step 4: Testing the Model
In this section, we will test a trained model using sample data, analyze the results, and export the findings.
Step 4.1: Navigate to the Test Section
- In the left menu, click Test & Optimize and then Try New Data.
- This section allows you to test models with new datasets.
Step 4.2: Select Model and Data Sample List
- Choose the trained model (referred to as Trained Tool) and select the Data Sample List you want to test.
- Click the Accuracy Test button to start a test job.
Note:
- To test the model on a blind dataset, you must upload and segment the data (see Sections 1 & 2).
- In this tutorial, we will test the model against the same dataset used for training.
Step 4.3: Wait for Test Job Completion
- After triggering the test, wait 2–3 minutes and refresh the page.
- Click the Trial Results tab to view the results.
Note:
- The test duration varies based on dataset size.
- A 1 GB dataset may take approximately 10 minutes to complete.
Step 4.4: View Regression Plot
- Click the second option button (highlighted in the UI) to view the Regression Plot.
- Refer to Section 3.8 for details on interpreting these plots.
Step 4.5: Review Test Statistics
- The statistics will be displayed in a format similar to AI Explore results.
- If the test data includes labeled values, a Regression Plot will be generated.
- If no labeled data is provided, no plot will be produced, but you can still export raw results.
Step 4.6: Export Results
- Click Show Sample Level Details (bottom left) to review detailed test data.
- To export the results, click Export to CSV.
Step 4.7: Understanding the Results
- Results: Predictions made by the Reality AI algorithm.
- Expected Results: Ground truth labels assigned during data upload.
Note:
- You can filter the view to display only correct or incorrect results.
- To analyze waveform data for each segment, go to the View Sample tab.
- This helps compare successful vs. unsuccessful predictions.
You have successfully completed this section.